
Space Cloud automatically scales your services to match the load on the system. Each service is scaled independently of each other.
The following parameters are required for autoscaling to work.
The different types of scalers available in Space Cloud are:
You can specify multiple scalers for a single service in Space Cloud.
Each scaler calculates the desired number of instances for a service based on its type. For example, A CPU scaler will calculate the number of instances based on CPU consumption.
Space Cloud polls the number of instances from each scaler every few seconds, called the polling interval, which can be configured (default: 15 seconds).
If multiple scalers are configured for a single service, then Space Cloud uses the highest scale output from all the scalers and auto-scales your service accordingly. The desired scale value used by Space Cloud is always in the range of the min and max replicas specified by you for the service.
For example, if you have configured both the CPU and Memory scaler for a service, and the calculated number of instances as per these scalers are 4 and 5 respectively. Then, Space Cloud will enforce 5 as the desired scale.
Autoscaling works for each service independently. This feature makes sure that each service can scale independent of the other, keeping the system highly reactive.
To configure the auto-scaling config of service, head over to the Deployments section in Mission Control:
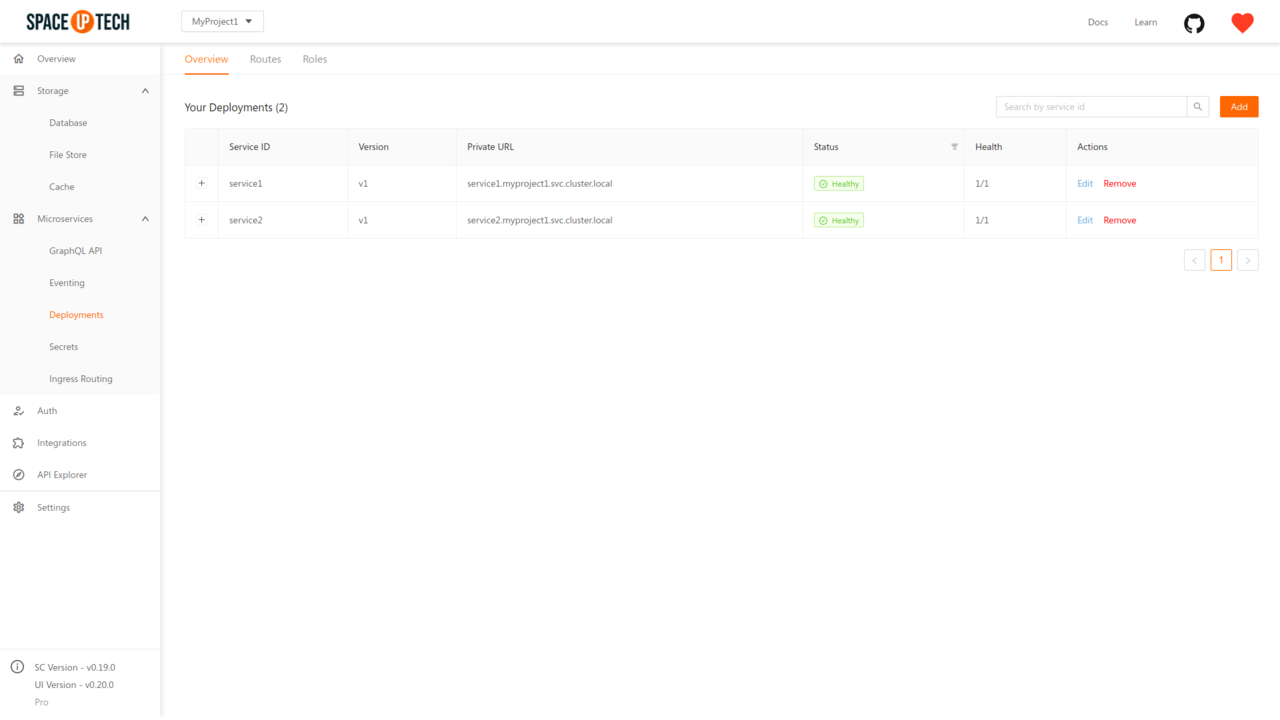
Click on the Edit button beside the required service to open the service configuration page. Expand the Advanced section to see the following configs:
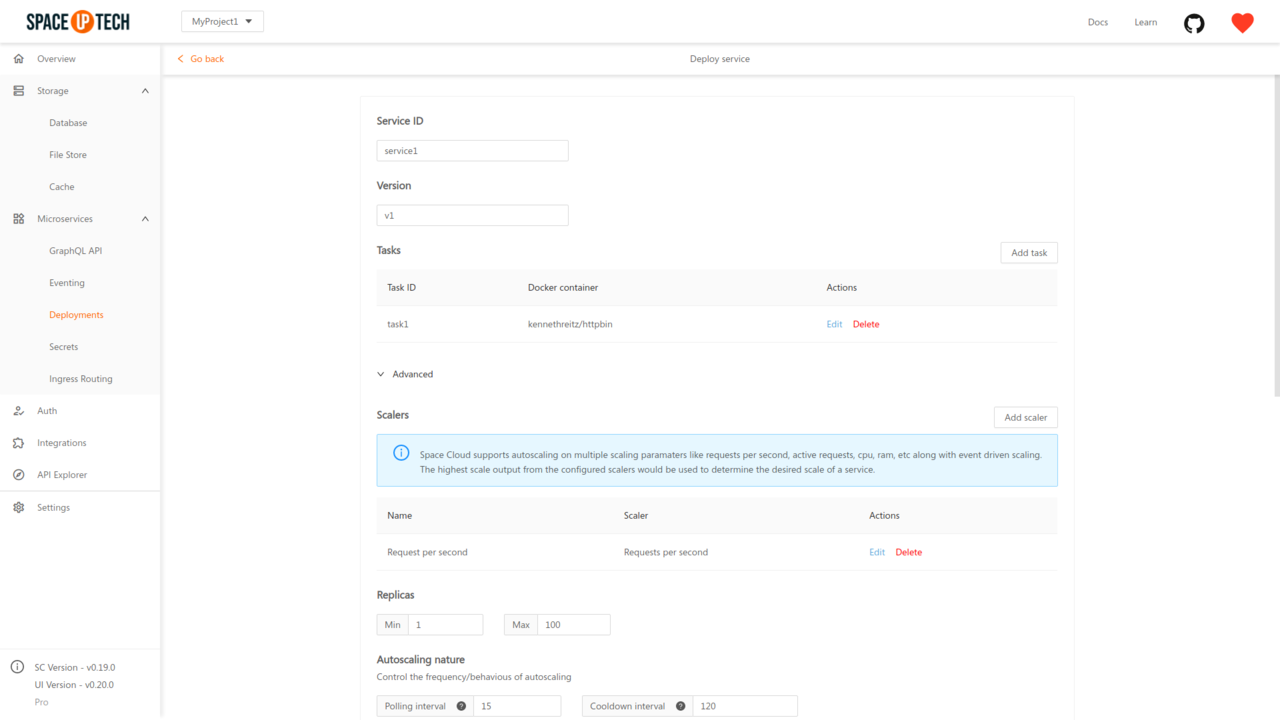
Set the min and max replicas as per your needs.
Then configure the scalers for the service. Mission Control, by default configures the Request per second scaler for your service so that you can get started without thinking about auto-scaling in most use cases.
However, if you want to change the behaviour of autoscaling, you can edit/remove the existing scaler and/or add new scalers as per your requirement.
To add a scaler, click on the Add scaler button to open the following form:
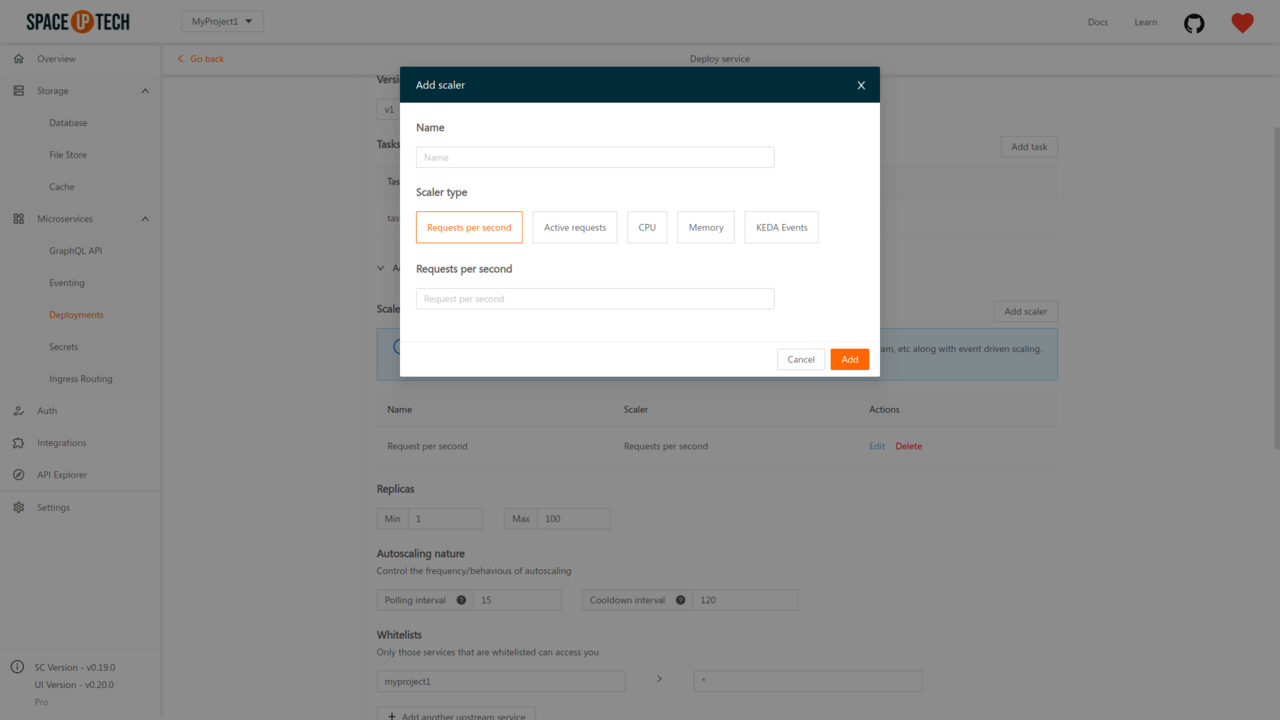
Select the appropriate scaler type and configure it as per your requirements.
The configuration for the scalers is explained below in detail.
To scale based on the number of request per second, choose the scaler type as Request per second:

Provide the number of requests per second you desire for an instance and save the scaler config.
For example, if you have configured the number of requests per second to be 80, and there are 200 requests per second for your service, then Space Cloud will scale the number of instances to 3 (200/80).
If you want to scale on the number of active/concurrent requests to your service, then choose the scaler type as Active requests:
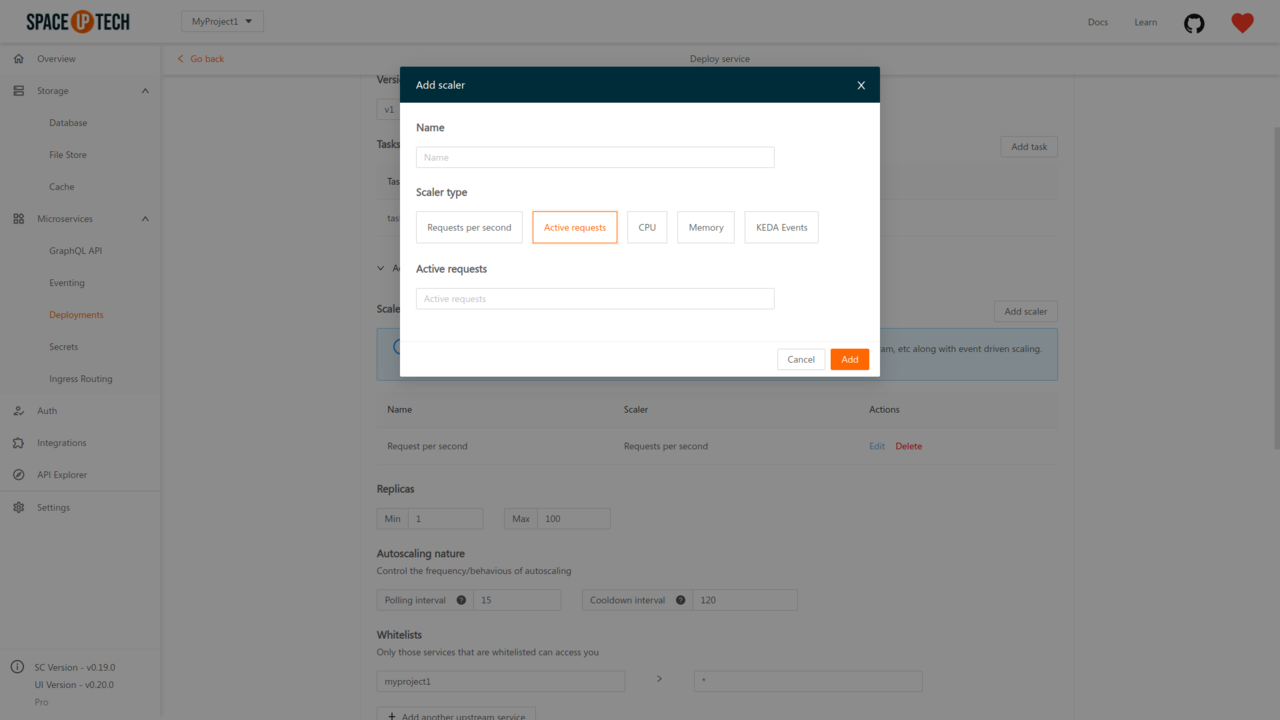
Provide the number of active requests desired for an instance and save the scaler config.
If you want to scale based on CPU consumption, select the scaler type as CPU:
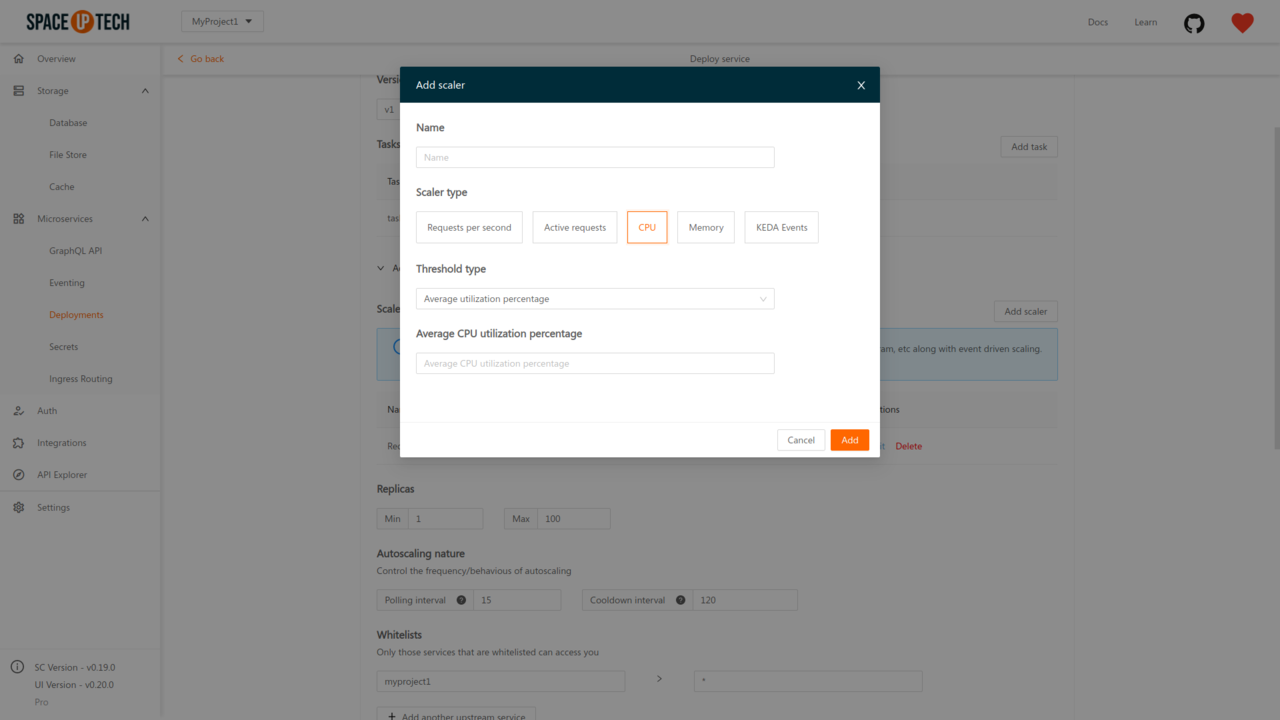
Select a threshold type. There are 3 types of thresholds:
After selecting a threshold type, provide a value for that threshold.
The threshold value for Average utilization percentage has to be an integer between 0 and 100, denoting the desired average CPU utilization percentage.
For average/total value, the threshold value should be a string denoting the number of CPU cores in millis. For example, 100m means 0.1 cpu core.
If you want to scale based on memory consumption, select the scaler type as Memory:
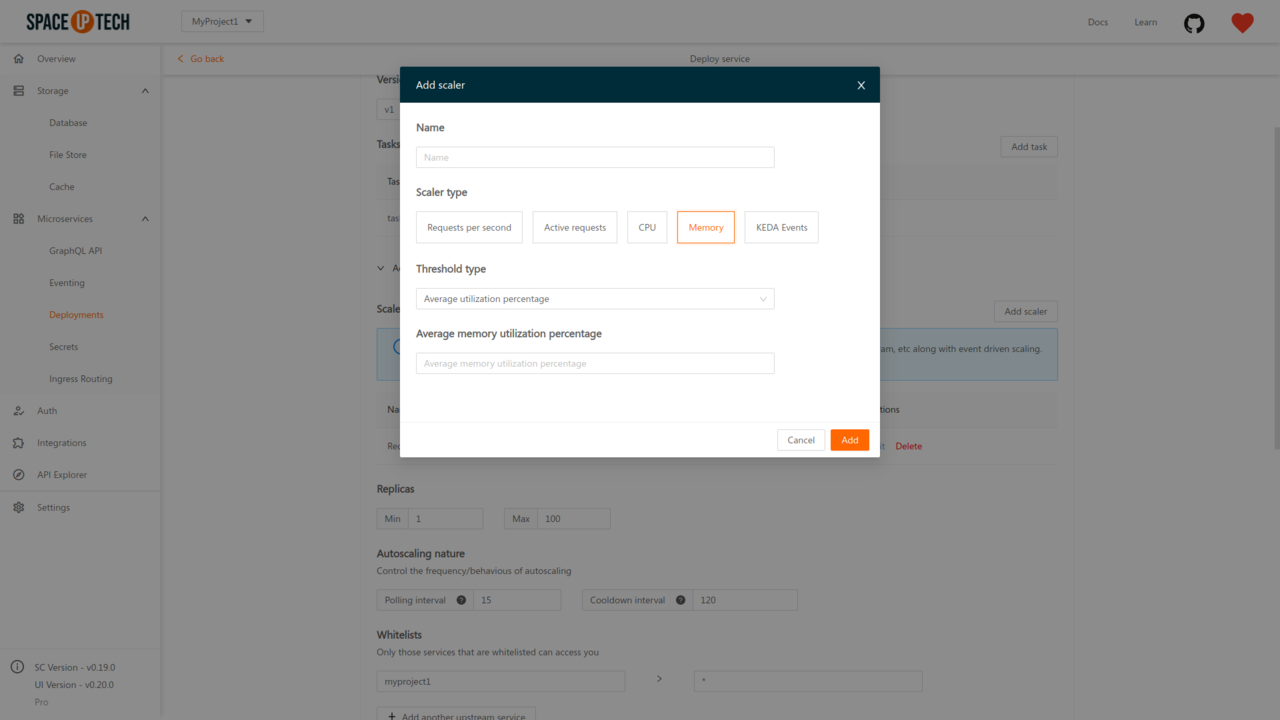
Select a threshold type. There are 3 types of thresholds:
After selecting a threshold type, provide a value for that threshold.
The threshold value for Average utilization percentage has to be an integer between 0 and 100, denoting the desired average memory utilization percentage.
For average/total value, the threshold value should be a string denoting the amount of memory (Example: 100Mi, 45656Ki, 0.5Gi).
Space Cloud comes packed with KEDA (Kubernetes Event-Driven Autoscaling) to autoscale on the basis of various metrics.
For example, using KEDA events, you can easily scale on the basis of a cron schedule or the number of pending items in a broker, etc. Check out the complete list of scalers in KEDA.
To learn more about how KEDA works and its concepts, check out the documentation of KEDA.
To configure a KEDA scaler, select the scaler type as KEDA Events:
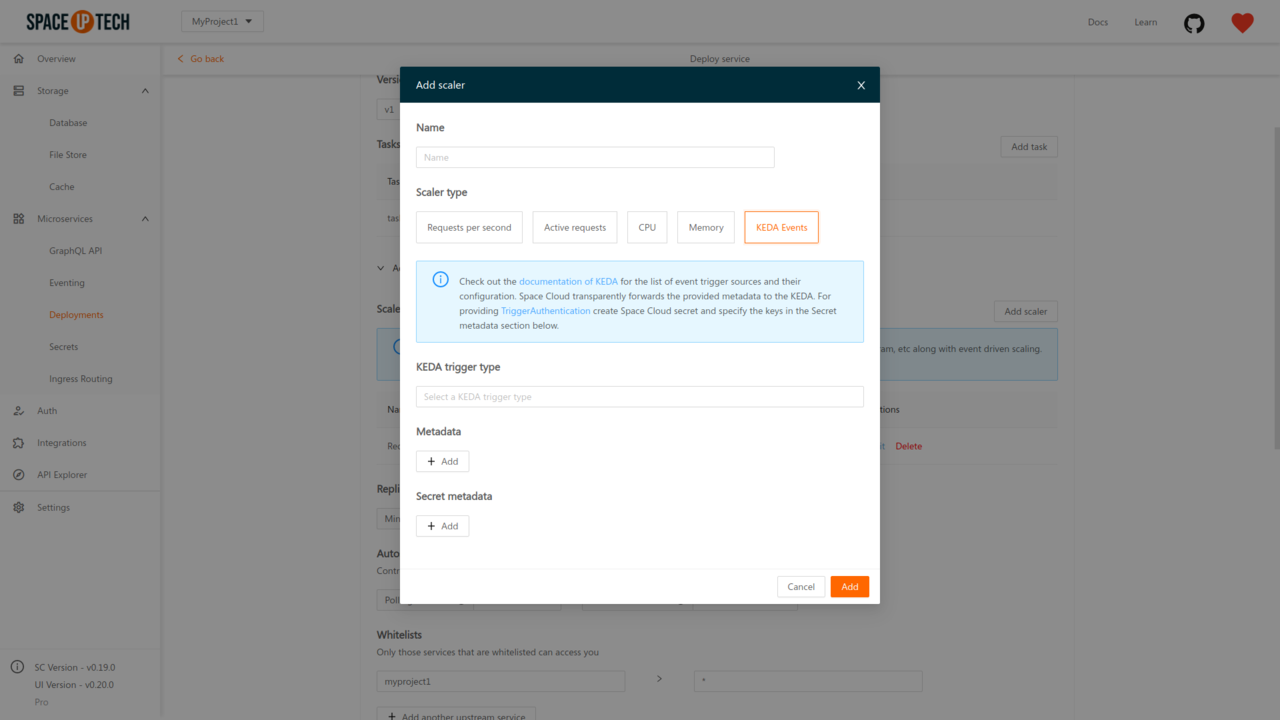
Select the KEDA trigger type first and then add the metadata (config) fields required for that scaler. The metadata required for each trigger type is well documented on KEDA’s documentation.
Using secret metadata:
Often metadata will include certain secrets. For example, the credentials of the database or a token, etc. Such values should be provided as secret metadata.
To use secret metadata, first create a secret in Space Cloud with the key-value pairs that you want to use in secret metadata. Then in the secret metadata section provide the value of the required metadata field as secrets.<secret-name>.<key>.
For example, let’s say you want username and password metadata fields as secret. Then first create a secret in Space Cloud with secret type as Environment Variables, name as kedaSecrets (name can be anything) and add the following key-value pairs:
username, Value: <username>password, Value: <password>Then add the following secret metadata in KEDA scaler config:
username, Value: secrets.kedaSecrets.usernamepassword, Value: secrets.kedaSecrets.passwordThere are two advanced options in the auto-scaling config:
The interval (in seconds) at which Space Cloud polls the desired scale output from the scalers. Default is 15 seconds.
Scaling from zero to one is an expensive operation. It can usually take a couple of seconds to a minute or two for a service to be scaled up from zero to one.
Hence Space Cloud waits for a while before it scales down service to zero. The interval for which it waits is known as cooldown interval (default: 120 seconds). If in this interval, the desired scale for the service changes, the scale down to zero operation is cancelled.