
Space Cloud supports JWT based authentication. Hence, integrating your custom auth services with Space Cloud is a straight forward task. Check out how JWT based authentication works in Space Cloud to learn more about it.
Whenever users make a signup/signin request, your auth service signs a token and provide it to your users.
The supported signing algorithms as of now are HS256 and RS256. This answer on StackOverflow is a good resource to decide whether you should use HSA or RSA based algorithm for signing tokens.
Thereafter, the user should provide the token in each request to Space Cloud. For HTTP requests, the token should be present inside Authorization header as Bearer <token>, whereas for websocket requests, the token should be present in the data.token key of the message body.
You need to ensure that Space Cloud is configured with the same secret that is used by your auth service for signing tokens. Check out the section for configuring JWT secrets in Space Cloud.
Based on the resource that the user is trying to access and the security rules you have configured for that resource, Space Cloud will validate the token and enforce your access control logic. Check out the security rules to learn more about the possibilities of access control in Space Cloud.
To add expiry to your tokens, you should set the exp field of the JWT claims in your auth service. The value of the exp field should be the time since epoch in seconds.
Example:
{
"role": "user",
"id": "1",
"exp": 1516239022
}
Space Cloud will consider a token to be valid based on the following criteria:
exp claim, then its value should be greater than the current time (in seconds since epoch).Rotating secrets with Space Cloud is pretty easy as Space Cloud supports multiple secrets.
Steps to rotate secrets:
If your auth service is providing JWTs to multiple apps, it’s essential to verify the audience of the JWT. Failing to do so is a major security vulnerability.
You should set the aud claim of the JWTs in your auth service to specify the intended audience of the JWT.
Then you should set the audience field in the secrets configuration of Space Cloud.
To set the audience field, check the Check audience option in the Advanced section while adding a JWT secret, and specify the intended audience value there:
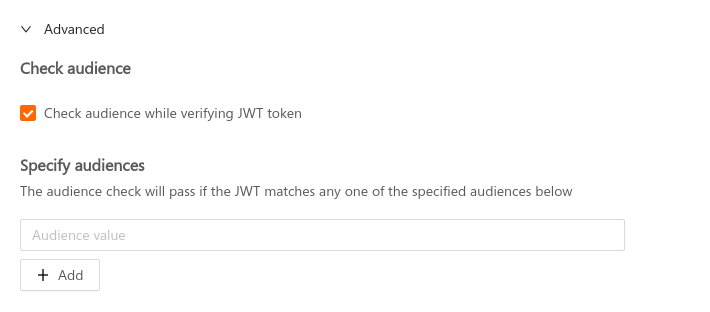
Space Cloud supports specifying multiple audiences for a secret.
The audience check will pass if the value in the aud field of JWT matches with any one of the specified audiences. If the aud field in the JWT is an array of audiences (string), then the audience check passes if any of the audience in the aud field matches with any one of the secified audiences.
In certain rare scenarios, you might have multiple auth services for different applications, all using the same secret for signing the JWTs.
In such a case, you might want to validate the issuer of the JWT as well. To do so, you should set the iss field of the JWT in your auth service, specifying the issuer of the JWT.
Then you should set the issuer field in the secrets configuration of Space Cloud.
To set the issuer field, check the Check issuer option in the Advanced section while adding a JWT secret, and specify the issuer value there:
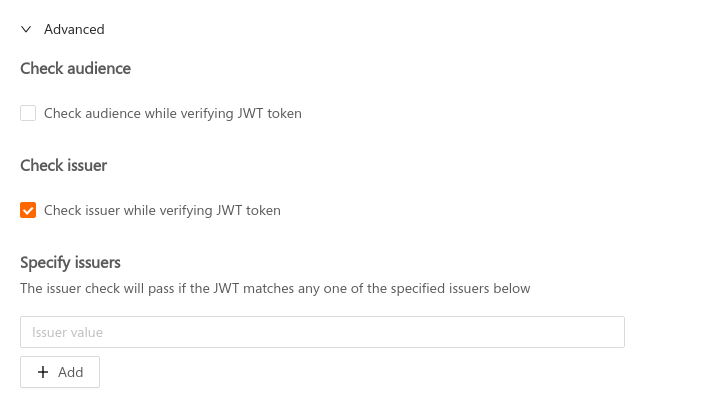
Space Cloud supports specifying multiple issuers for a secret.
The issuer check will pass if the value in the iss field of JWT matches with any one of the specified issuers. If the iss field in the JWT is an array of issuers (string), then the issuer check passes if any of the issuers in the iss field matches with any one of the specified issuers.