
Head over to the Project settings tab in the Settings section of Mission Control. You would see a JWT secrets section there:
Click on the add button there to open the following modal:
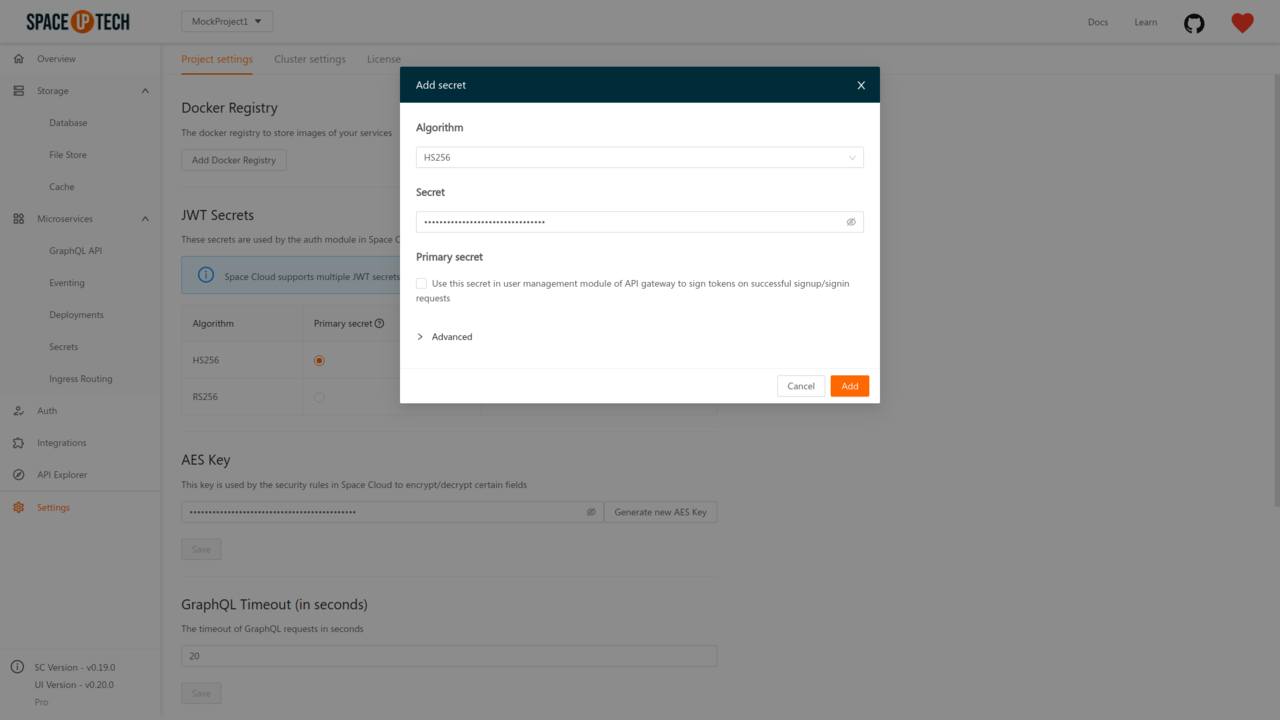
Space Cloud supports four types of secrets as of now, which are explained in detail below.
If your auth server is using HMAC-SHA256 for signing the JWTs, select the type as HS256 and provide the secret used while signing.
If your auth server is using RSA with SHA256 for signing the JWTS, select the type as RS256 and provide the private key used by your auth server for signing the JWTS.
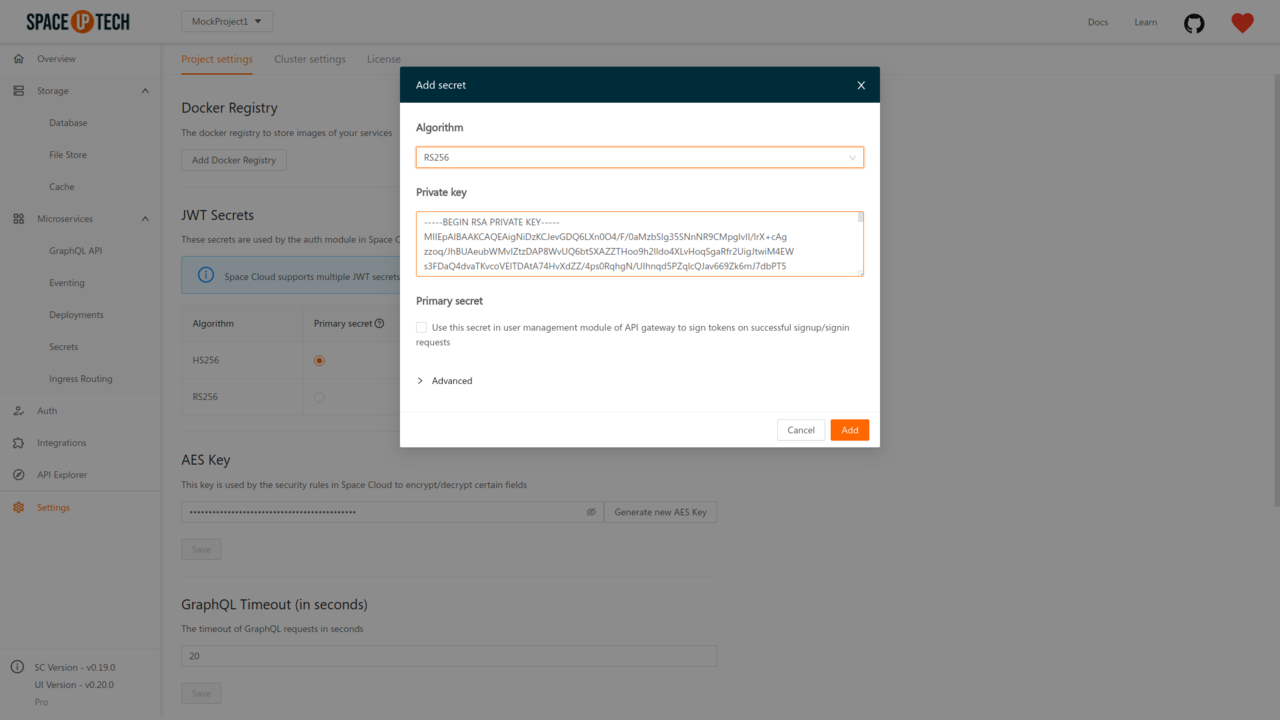
Mission Control automatically generates the public key from the private key and configures the Space Cloud with both the private and public keys.
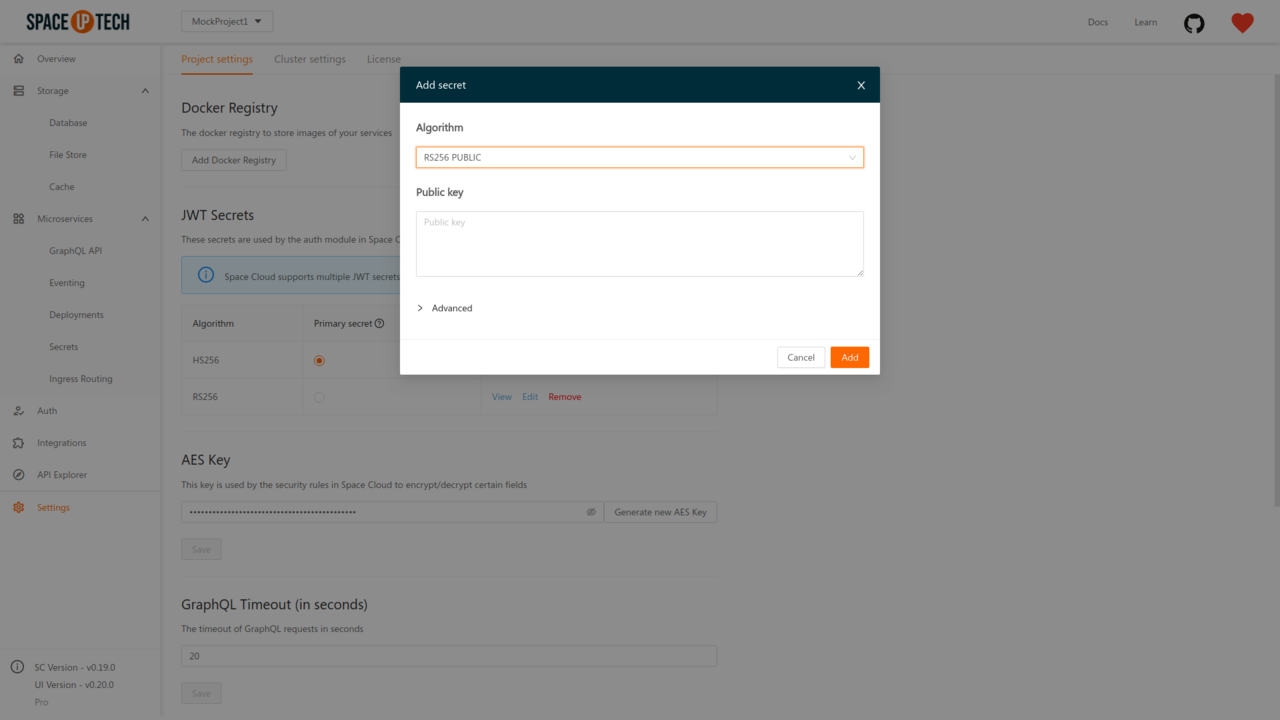
If you don’t have access to the private key, then you can use the RSA256 PUBLIC type.
You should select this type when your auth server is using RSA with SHA256 for signing the JWTS; however, you only have access to the public key and not the private key. Once you select this type, you can add the public key, as shown below:
Many third-party auth services provide a JWK URL where they publish their JWKs (JSON Web Keys used for signing the JWTs). The URL must publish the JWKs in the standard format as described in https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7517.
To integrate with such auth services, select the type as JWK URL and provide the JWK URL of your auth service:
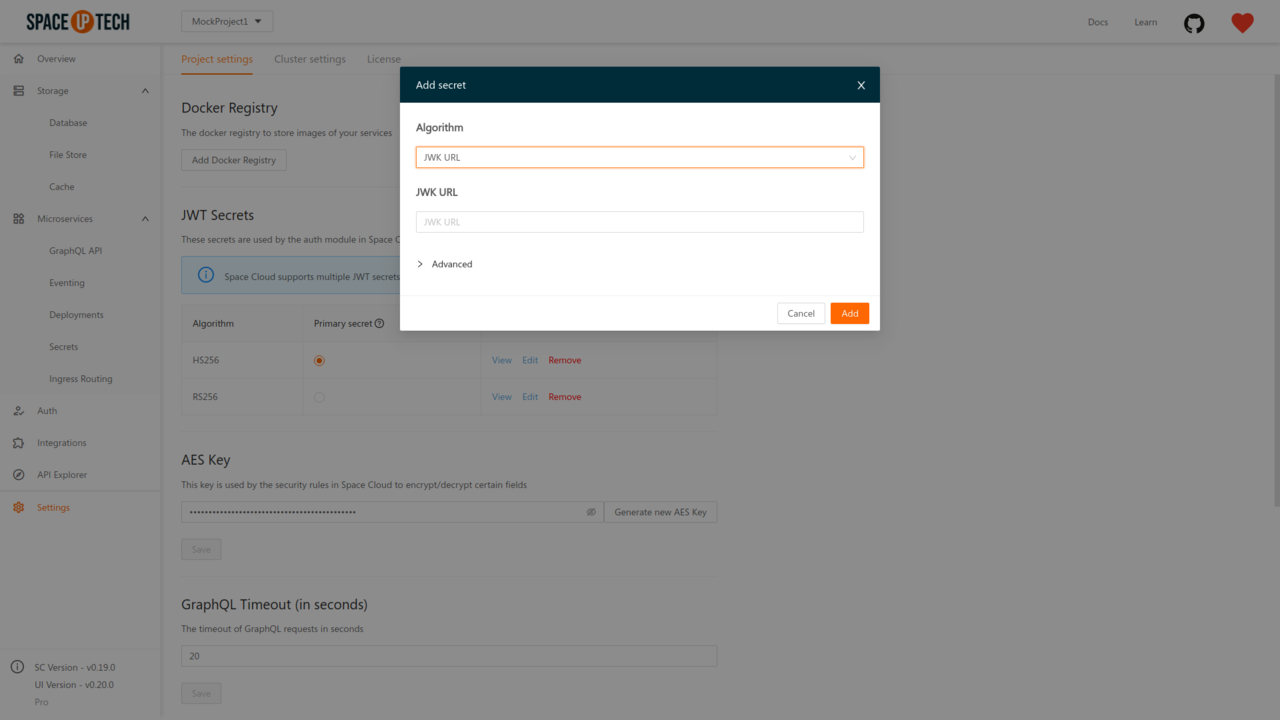
Check out the docs for integrating with third-party auth services to learn the URL formats and security considerations for the popular auth services like Firebase Auth, Auth0, etc.
Once a JWK URL is provided, Space Cloud automatically syncs the JWKS from the auth service to itself.
Rotating JWKs
Some providers rotate their JWKs (e.g. Firebase). If the provider sends
max-age or s-maxage in Cache-Control headerExpires headerwith the response of JWK, then Space Cloud will refresh the JWKs automatically. If the provider does not send the above, the JWKs are not refreshed.
Example JWK URL:
https://www.googleapis.com/service_accounts/v1/jwk/securetoken@system.gserviceaccount.com.https://<your-auth0-domain>.auth0.com/.well-known/jwks.json.Certain JWT providers share JWKs between multiple tenants (like Firebase). They use the aud claim of JWT to specify the intended tenant for the JWT.
In these case, you MUST set the audience field to the appropriate value. Failing to do so is a major security vulnerability.
Setting the audience field in the secrets configuration will make sure that the aud claim from the JWT is also checked during verification. Not doing this check will allow JWTs issued for other tenants to be valid as well.
To set the audience field, check the Check audience option in the Advanced section while adding a JWT secret, and specify the intended audience value there:
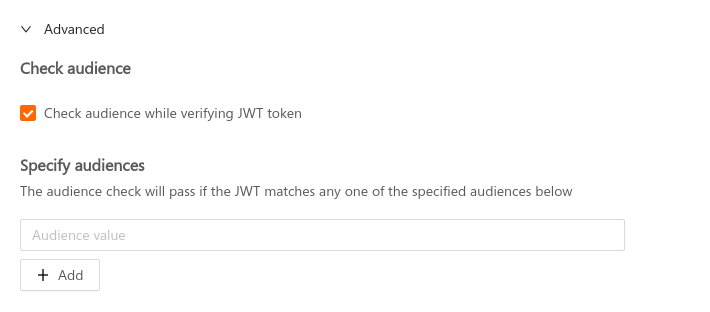
Space Cloud supports specifying multiple audiences for a secret. The audience check will pass if the value in the aud field of JWT matches with any one of the specified audiences. If the aud field in the JWT is an array of audiences (string), then the audience check passes if any of the audience in the aud field matches with any one of the specified audiences.
Certain JWT providers set the iss field of the JWT so that the issuer of the JWT provider can be verified.
Setting the issuer field in the secrets configuration of Space Cloud will make sure that the iss claim from the JWT is also checked during verification. This is an additional security check which must be enforced if the JWT provider supports it.
To set the issuer field, check the Check issuer option in the Advanced section while adding a JWT secret, and specify the issuer value there:
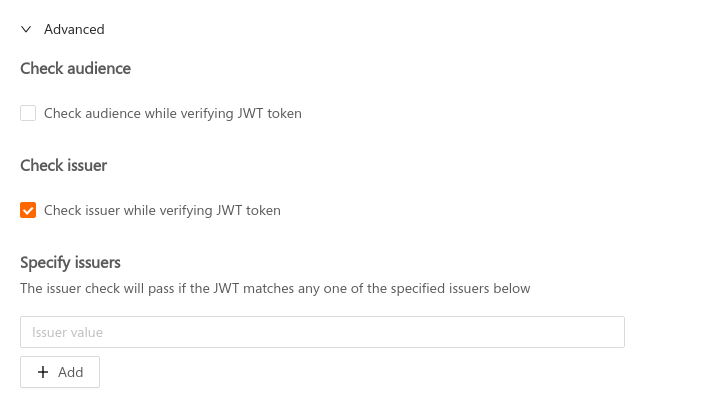
Space Cloud supports specifying multiple issuers for a secret. The issuer check will pass if the value in the iss field of JWT matches with any one of the specified issuers. If the iss field in the JWT is an array of issuers (string), then the issuer check passes if any of the issuers in the iss field matches with any one of the specified issuers.
A primary secret is used by Space Cloud to sign JWTs for various operations internally. Hence one of the specified secrets needs to be marked as a primary secret.
By default, when you create a project via Mission Control, it automatically configures an HSA256 secret to be the primary secret.
If you need to change the primary secret, then check the Primary secret option while adding a secret via Mission Control.
If you want to set one of the existing secrets to be the primary secret, check the radio button for the corresponding secret in the Primary secret column from the JWT secrets table:
